Lowest Common Ancestor - Farach-Colton and Bender Algorithm¶
Let $G$ be a tree. For every query of the form $(u, v)$ we want to find the lowest common ancestor of the nodes $u$ and $v$, i.e. we want to find a node $w$ that lies on the path from $u$ to the root node, that lies on the path from $v$ to the root node, and if there are multiple nodes we pick the one that is farthest away from the root node. In other words the desired node $w$ is the lowest ancestor of $u$ and $v$. In particular if $u$ is an ancestor of $v$, then $u$ is their lowest common ancestor.
The algorithm which will be described in this article was developed by Farach-Colton and Bender. It is asymptotically optimal.
Algorithm¶
We use the classical reduction of the LCA problem to the RMQ problem. We traverse all nodes of the tree with DFS and keep an array with all visited nodes and the heights of these nodes. The LCA of two nodes $u$ and $v$ is the node between the occurrences of $u$ and $v$ in the tour, that has the smallest height.
In the following picture you can see a possible Euler-Tour of a graph and in the list below you can see the visited nodes and their heights.
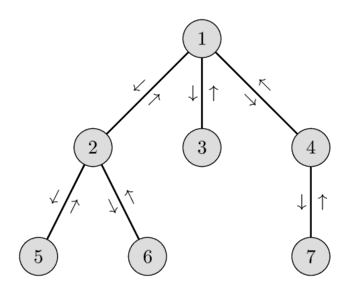
You can read more about this reduction in the article Lowest Common Ancestor. In that article the minimum of a range was either found by sqrt-decomposition in $O(\sqrt{N})$ or in $O(\log N)$ using a Segment tree. In this article we look at how we can solve the given range minimum queries in $O(1)$ time, while still only taking $O(N)$ time for preprocessing.
Note that the reduced RMQ problem is very specific: any two adjacent elements in the array differ exactly by one (since the elements of the array are nothing more than the heights of the nodes visited in order of traversal, and we either go to a descendant, in which case the next element is one bigger, or go back to the ancestor, in which case the next element is one lower). The Farach-Colton and Bender algorithm describes a solution for exactly this specialized RMQ problem.
Let's denote with $A$ the array on which we want to perform the range minimum queries. And $N$ will be the size of $A$.
There is an easy data structure that we can use for solving the RMQ problem with $O(N \log N)$ preprocessing and $O(1)$ for each query: the Sparse Table. We create a table $T$ where each element $T[i][j]$ is equal to the minimum of $A$ in the interval $[i, i + 2^j - 1]$. Obviously $0 \leq j \leq \lceil \log N \rceil$, and therefore the size of the Sparse Table will be $O(N \log N)$. You can build the table easily in $O(N \log N)$ by noting that $T[i][j] = \min(T[i][j-1], T[i+2^{j-1}][j-1])$.
How can we answer a query RMQ in $O(1)$ using this data structure? Let the received query be $[l, r]$, then the answer is $\min(T[l][\text{sz}], T[r-2^{\text{sz}}+1][\text{sz}])$, where $\text{sz}$ is the biggest exponent such that $2^{\text{sz}}$ is not bigger than the range length $r-l+1$. Indeed we can take the range $[l, r]$ and cover it two segments of length $2^{\text{sz}}$ - one starting in $l$ and the other ending in $r$. These segments overlap, but this doesn't interfere with our computation. To really achieve the time complexity of $O(1)$ per query, we need to know the values of $\text{sz}$ for all possible lengths from $1$ to $N$. But this can be easily precomputed.
Now we want to improve the complexity of the preprocessing down to $O(N)$.
We divide the array $A$ into blocks of size $K = 0.5 \log N$ with $\log$ being the logarithm to base 2. For each block we calculate the minimum element and store them in an array $B$. $B$ has the size $\frac{N}{K}$. We construct a sparse table from the array $B$. The size and the time complexity of it will be:
Now we only have to learn how to quickly answer range minimum queries within each block. In fact if the received range minimum query is $[l, r]$ and $l$ and $r$ are in different blocks then the answer is the minimum of the following three values: the minimum of the suffix of block of $l$ starting at $l$, the minimum of the prefix of block of $r$ ending at $r$, and the minimum of the blocks between those. The minimum of the blocks in between can be answered in $O(1)$ using the Sparse Table. So this leaves us only the range minimum queries inside blocks.
Here we will exploit the property of the array. Remember that the values in the array - which are just height values in the tree - will always differ by one. If we remove the first element of a block, and subtract it from every other item in the block, every block can be identified by a sequence of length $K - 1$ consisting of the number $+1$ and $-1$. Because these blocks are so small, there are only a few different sequences that can occur. The number of possible sequences is:
Thus the number of different blocks is $O(\sqrt{N})$, and therefore we can precompute the results of range minimum queries inside all different blocks in $O(\sqrt{N} K^2) = O(\sqrt{N} \log^2(N)) = O(N)$ time. For the implementation we can characterize a block by a bitmask of length $K-1$ (which will fit in a standard int) and store the index of the minimum in an array $\text{block}[\text{mask}][l][r]$ of size $O(\sqrt{N} \log^2(N))$.
So we learned how to precompute range minimum queries within each block, as well as range minimum queries over a range of blocks, all in $O(N)$.
With these precomputations we can answer each query in $O(1)$, by using at most four precomputed values: the minimum of the block containing l, the minimum of the block containing r, and the two minima of the overlapping segments of the blocks between them.
Implementation¶
int n;
vector<vector<int>> adj;
int block_size, block_cnt;
vector<int> first_visit;
vector<int> euler_tour;
vector<int> height;
vector<int> log_2;
vector<vector<int>> st;
vector<vector<vector<int>>> blocks;
vector<int> block_mask;
void dfs(int v, int p, int h) {
first_visit[v] = euler_tour.size();
euler_tour.push_back(v);
height[v] = h;
for (int u : adj[v]) {
if (u == p)
continue;
dfs(u, v, h + 1);
euler_tour.push_back(v);
}
}
int min_by_h(int i, int j) {
return height[euler_tour[i]] < height[euler_tour[j]] ? i : j;
}
void precompute_lca(int root) {
// get euler tour & indices of first occurrences
first_visit.assign(n, -1);
height.assign(n, 0);
euler_tour.reserve(2 * n);
dfs(root, -1, 0);
// precompute all log values
int m = euler_tour.size();
log_2.reserve(m + 1);
log_2.push_back(-1);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
log_2.push_back(log_2[i / 2] + 1);
block_size = max(1, log_2[m] / 2);
block_cnt = (m + block_size - 1) / block_size;
// precompute minimum of each block and build sparse table
st.assign(block_cnt, vector<int>(log_2[block_cnt] + 1));
for (int i = 0, j = 0, b = 0; i < m; i++, j++) {
if (j == block_size)
j = 0, b++;
if (j == 0 || min_by_h(i, st[b][0]) == i)
st[b][0] = i;
}
for (int l = 1; l <= log_2[block_cnt]; l++) {
for (int i = 0; i < block_cnt; i++) {
int ni = i + (1 << (l - 1));
if (ni >= block_cnt)
st[i][l] = st[i][l-1];
else
st[i][l] = min_by_h(st[i][l-1], st[ni][l-1]);
}
}
// precompute mask for each block
block_mask.assign(block_cnt, 0);
for (int i = 0, j = 0, b = 0; i < m; i++, j++) {
if (j == block_size)
j = 0, b++;
if (j > 0 && (i >= m || min_by_h(i - 1, i) == i - 1))
block_mask[b] += 1 << (j - 1);
}
// precompute RMQ for each unique block
int possibilities = 1 << (block_size - 1);
blocks.resize(possibilities);
for (int b = 0; b < block_cnt; b++) {
int mask = block_mask[b];
if (!blocks[mask].empty())
continue;
blocks[mask].assign(block_size, vector<int>(block_size));
for (int l = 0; l < block_size; l++) {
blocks[mask][l][l] = l;
for (int r = l + 1; r < block_size; r++) {
blocks[mask][l][r] = blocks[mask][l][r - 1];
if (b * block_size + r < m)
blocks[mask][l][r] = min_by_h(b * block_size + blocks[mask][l][r],
b * block_size + r) - b * block_size;
}
}
}
}
int lca_in_block(int b, int l, int r) {
return blocks[block_mask[b]][l][r] + b * block_size;
}
int lca(int v, int u) {
int l = first_visit[v];
int r = first_visit[u];
if (l > r)
swap(l, r);
int bl = l / block_size;
int br = r / block_size;
if (bl == br)
return euler_tour[lca_in_block(bl, l % block_size, r % block_size)];
int ans1 = lca_in_block(bl, l % block_size, block_size - 1);
int ans2 = lca_in_block(br, 0, r % block_size);
int ans = min_by_h(ans1, ans2);
if (bl + 1 < br) {
int l = log_2[br - bl - 1];
int ans3 = st[bl+1][l];
int ans4 = st[br - (1 << l)][l];
ans = min_by_h(ans, min_by_h(ans3, ans4));
}
return euler_tour[ans];
}